| dc.contributor.author | Jullien, D. | fr_FR |
| dc.contributor.author | Sarret, Y. | fr_FR |
| dc.contributor.author | Stamm, C. | fr_FR |
| dc.contributor.author | Schmitt, D. | fr_FR |
| dc.date.accessioned | 2013-02-18T16:18:02Z | |
| dc.date.available | 2013-02-18T16:18:02Z | |
| dc.date.issued | 1993 | fr_FR |
| dc.identifier.citation | Jullien, D. ; Sarret, Y. ; Stamm, C. ; Schmitt, D., Mécanique et régulation de la migration kératinocytaire, Med Sci (Paris), 1993, Vol. 9, N° 4; p.403-411 | fr_FR |
| dc.identifier.issn | 1958-5381 | fr_FR |
| dc.identifier.uri | http://hdl.handle.net/10608/2933 | |
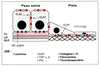
| dc.description.abstract | During cutaneous wound healing, basal keratinocytes migrate laterally to cover the wound bed, whereas in an unwounded situation they move vertically and differentiate to constitute the different layers of the epidermis. Many extracellular factors influence the behavior of these cells. The main ones are extracellular matrix molecules and cytokines present in the dermoepidermal junction and/or in the wound bed. Some of them such as collagens type I and IV, fibronectin and epidermal growth factor are known to induce basal keratinocyte migration. On the contrary, others, such as laminin, inhibit it. Molecules from the VIA-integrin family are receptors for many of these extracellular matrix molecules. As specific adhesion and signal transduction molecules, they play a critical role in keratinocyte migration by allowing interactions between the cell cytoskeleton and the macromolecules in the wound bed. This type of interaction is commonly seen in all the models of cell migration reviewed herein. These models try to explain the different mechanisms involved in basal keratinocyte migration. The translation of this phenomenon, at a light microscopic level is the extension of the lamellipodia/fillopodia at the leading edge of the cell. Finally, we present some dinical applications of the cumulative knowledge published in this field in basic science journals. | fr |
| dc.language.iso | fr | fr_FR |
| dc.publisher | John Libbey Eurotext, Montrouge | fr_FR |
| dc.rights | Article en libre accès | fr |
| dc.rights | Médecine/Sciences - Inserm - SRMS | fr |
| dc.source | M/S. Médecine sciences [revue papier, ISSN : 0767-0974], 1993, Vol. 9, N° 4; p.403-411 | fr_FR |
| dc.title | Mécanique et régulation de la migration kératinocytaire | fr |
| dc.type | Article | fr_FR |
| dc.identifier.doi | 10.4267/10608/2933 | |