| dc.contributor.author | Wang, Shumei | - |
| dc.contributor.author | Qiu, Liyun | - |
| dc.contributor.author | Meng, Xianguang | - |
| dc.contributor.author | Dang, Ningning | - |
| dc.date.accessioned | 2019-11-05T12:51:52Z | |
| dc.date.available | 2019-11-05T12:51:52Z | |
| dc.date.issued | 2018 | |
| dc.identifier.citation | Wang, Shumei ; Qiu, Liyun ; Meng, Xianguang ; Dang, Ningning ; Knock-down of filaggrin influences the mitogen-activated protein kinases signaling pathway in normal human epidermal keratinocytes, Med Sci (Paris), , Vol. 34, N° HS ; p. 94-98 ; DOI : 10.1051/medsci/201834f116 | |
| dc.identifier.issn | 1958-5381 | |
| dc.identifier.uri | http://hdl.handle.net/10608/9993 | |
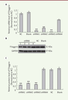
| dc.description.abstract | Background: Filaggrin is an essential structural protein of the stratum corneum binding to the keratin intermediate filaments to form a dense protein-lipid matrix. However, the function of filaggrin in epidermal terminal differentiation is not completely understood. Aim: To evaluate the effects of filaggrin on normal human epidermal keratinocytes (NHEKs) and to investigate the relevant mechanisms. Methods: Short hairpin RNA (shRNA) technology was used to knock-down filaggrin in normal human epidermal keratinocytes (NHEKs). Western blot and real-time quantitative PCR (qRT-PCR) were performed to detect expression of filaggrin, differentiation-related proteins and MAPK-related proteins. Results: Filaggrin was successfully knocked down in NHEKs (99% efficiency). We found that the lack of filaggrin significantly decreased the expression of some differentiation-related proteins, including Cytokeratin 5 protein, Cytokeratin 14 protein, ST14 protein and SPRR3 protein (P<0.05). In addition, filaggrin knock-down significantly decreased expression of p-p38, p-ERK1/2, p-JNK, p-Akt, and p-NF-κB in NHEKs. Conclusion: Our study shows that filaggrin regulates epidermal terminal differentiation and impairs MAPK signaling pathway in normal human epidermal keratinocytes. | en |
| dc.language.iso | en | |
| dc.publisher | EDP Sciences | |
| dc.rights | Article en libre accès | fr |
| dc.rights | Médecine/Sciences - Inserm - SRMS | fr |
| dc.source | M/S. Médecine sciences [ISSN papier : 0767-0974 ; ISSN numérique : 1958-5381], , Vol. 34, N° HS; p. 94-98 | |
| dc.title | Knock-down of filaggrin influences the mitogen-activated protein kinases signaling pathway in normal human epidermal keratinocytes | en |
| dc.type | Article | |
| dc.contributor.affiliation | Department of Community Medicine, Jinan Central Hospital affiliated to Shandong University, No.105 Jiefang Road, Jinan 250013, Shandong Province, China | |
| dc.contributor.affiliation | Department of Pharmacy, Jinan Central Hospital affiliated to Shandong University, No.105 Jiefang Road, Jinan 250013, Shandong Province, China | |
| dc.contributor.affiliation | Department of Dermatology, Jinan Central Hospital affiliated to Shandong University, No.105 Jiefang Road, Jinan 250013, Shandong Province, China | |
| dc.identifier.doi | 10.1051/medsci/201834f116 | |