| dc.contributor.author | Junjie, Yan | - |
| dc.contributor.author | Weidong, Liu | - |
| dc.contributor.author | Ren, Lin | - |
| dc.contributor.author | Min, Ye | - |
| dc.date.accessioned | 2019-11-05T12:51:31Z | |
| dc.date.available | 2019-11-05T12:51:31Z | |
| dc.date.issued | 2018 | |
| dc.identifier.citation | Junjie, Yan ; Weidong, Liu ; Ren, Lin ; Min, Ye ; Incidence and risk factors of the temporomandibular joint disorders in the patients without condylar fractures, Med Sci (Paris), , Vol. 34, N° HS ; p. 39-42 ; DOI : 10.1051/medsci/201834f107 | |
| dc.identifier.issn | 1958-5381 | |
| dc.identifier.uri | http://hdl.handle.net/10608/9984 | |
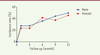
| dc.description.abstract | Objective: To evaluate the incidence and risk factors of the temporomandibular joint disorders (TMD) in the patients suffering from maxillo-facial injury without condylar fractures. Methods: sixty patients without condylar fractures were recruited from Feb 2014 to Nov 2015 in the department of stomatology, Lishui people’s hospital. The incidence of TMD was recorded at 1, 3, 6, 9 and 12 months after injury through MRI examination. The risk factors for TMD were evaluated by logistic regression analysis. Results: the TMD incidence rates were 25.0%, 30.0%, 35.0%, 41.7% and 48.3% at 1, 3, 6, 9 and 12 months after injury with no statistical difference between male and female (P>0.05). Logistic regression indicated that disorder of occlusal relationship (OR=1.84,95%CI:1.36-2.78) and hemi-mastication (OR=1.56, 95% CI:1.23- 2.24) were independent risk factors for the development of TMD. Conclusion: there was a high incidence of temporomandibular joint disorders in the patients suffering from maxillo-facial injury without condylar fractures. The disorder of occlusal relationship and hemi-mastication were independent risk factors for the development of post-injury TMD. | en |
| dc.language.iso | en | |
| dc.publisher | EDP Sciences | |
| dc.rights | Article en libre accès | fr |
| dc.rights | Médecine/Sciences - Inserm - SRMS | fr |
| dc.source | M/S. Médecine sciences [ISSN papier : 0767-0974 ; ISSN numérique : 1958-5381], , Vol. 34, N° HS; p. 39-42 | |
| dc.title | Incidence and risk factors of the temporomandibular joint disorders in the patients without condylar fractures | en |
| dc.type | Article | |
| dc.contributor.affiliation | Department of stomatology, Lishui people’s hospital (6th affiliated hospital of Wenzhou medical university) Zhejian Lishui, No.15 Dazhong Road, Liandu District, Lishui City, Zhejiang Province 323000 PR China. | |
| dc.identifier.doi | 10.1051/medsci/201834f107 | |