La leptine : une clef pour la reproduction.
Date
1999Auteur
Bruneau, G
Vaisse, C
Caraty, A
Monget, P
Voir/
Metadata
Afficher la notice complèteRésumé
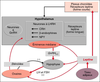
La leptine, hormone secretee par le tissu adipeux, agit par l' intermediaire de recepteurs dissemines dans l' organisme, Outre son role dans la satiete, l' equilibre energetique et la thermoregulation, elle tient une place centrale dans le developpement et la regulation de la reproduction. Dans l' hypothalamus, elle regle la secretion pulsatile de la LHRH (luteinizing hormone releasing hormone), dans l' hypophyse elle module la secretion des gonadotrophines ; elle agirait aussi directement sur les gonades. Chez les femelles, elle contribue largement au controle de l' ovulation, informant l' axe hypothalamo-hypophysaire des reserves energetiques qui sont une condition limitante pour mener a bien la fecondation, la gestation et la lactation. Leptin is a hormone synthesized by adipose tissue and acts at transmembrane receptors distributed throughout the body. Besides roles in food intake regulation, energy balance and thermoregulation, leptin stimulates the development and function of the reproductive axis. This effect is exerted mainly at the hypothalamic level to modify LHRH pulsatility through mechanisms that are poorly understood. In addition, leptin acts at the hypophysis to modulate gonadotrophin secretion and also directly on the gonads. In females, it contributes mainly to the control of ovulation by informing the hypothalamo-hypophysial axis about fat reserves; a limiting condition for the successful completion of fertilization, gestation and lactation. [References: 48]
Pour citer ce document
Bruneau, G - Vaisse, C - Caraty, A - Monget, P, La leptine : une clef pour la reproduction., Med Sci (Paris), 1999, Vol. 15, N° 2; p.191-6



