| dc.contributor.author | Flabeau, Olivier | - |
| dc.contributor.author | Bisson, Thomas | - |
| dc.date.accessioned | 2022-10-18T07:10:44Z | |
| dc.date.available | 2022-10-18T07:10:44Z | |
| dc.date.issued | 2021 | |
| dc.identifier.citation | Flabeau, Olivier ; Bisson, Thomas ; Le suivi multidisciplinaire de patients adultes atteints de dystrophie myotonique de type 1 dans le Sud Aquitain, Med Sci (Paris), Vol. 37, N° HS ; p. 32-35 ; DOI : 10.1051/medsci/2021190 | |
| dc.identifier.issn | 1958-5381 | |
| dc.identifier.uri | http://hdl.handle.net/10608/11975 | |
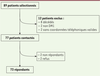
| dc.description.abstract | DM1 is characterized by a multisystemic involvement. Our objective was to determine the proportion of adequate follow-up for each affected organ in DM1 patients based on the recently published American and Spanish recommendations. To this end, we conducted a descriptive cross-sectional survey by phone in adult, genetically proven DM1 patients followed in the two French neuromuscular centers of Bayonne and Hendaye located in South Aquitaine, France. The questionnaire selected the most stringent criteria of the two international recommendations for each item of follow-up. Seventy-three patients were included, 55% of which were women (mean age of 48 years) with an average number of 467 CTG repeats. The proportion of patients receiving clinical follow-up in accordance with the recommendations was 90% in cardiology, 60% in neurology, 68% in ophthalmology, 53% in physiotherapy, 23% in pneumology, and 12% in rehabilitation. The high rate of neurological, cardiological, and ophthalmological monitoring might be explained by a locally dense medical demography whereas low rate of respiratory follow up and rehabilitation may reflect an incomplete knowledge of both the disease and the questionnaire. These results should be carefully interpretated as cognitive status may influence such a declarative study. Our study nevertheless disclosed important disparities according to the recommended multidisciplinary follow-up criteria in this French cohort of adult DM1 patients. These results highlight the major role of a multidisciplinary care and monitoring in DM1. | en |
| dc.language.iso | fr | |
| dc.publisher | EDP Sciences | |
| dc.relation.ispartof | Prise en charge | |
| dc.rights | Article en libre accès | fr |
| dc.rights | Médecine/Sciences - Inserm - SRMS | fr |
| dc.rights.uri | | |
| dc.source | M/S. Médecine sciences [ISSN papier : 0767-0974 ; ISSN numérique : 1958-5381], Vol. 37, N° HS; p. 32-35 | |
| dc.subject.mesh | Adulte | fr |
| dc.subject.mesh | Études de cohortes | fr |
| dc.subject.mesh | Études transversales | fr |
| dc.subject.mesh | Femelle | fr |
| dc.subject.mesh | France | fr |
| dc.subject.mesh | Humains | fr |
| dc.subject.mesh | Adulte d'âge moyen | fr |
| dc.subject.mesh | Dystrophie myotonique | fr |
| dc.subject.mesh | Techniques de physiothérapie | fr |
| dc.subject.mesh | thérapie | fr |
| dc.title | Le suivi multidisciplinaire de patients adultes atteints de dystrophie myotonique de type 1 dans le Sud Aquitain | fr |
| dc.title.alternative | Multidisciplinary care of patients with Myotonic Dystrophy type 1 (DM1) in South Aquitaine | en |
| dc.type | Article | |
| dc.contributor.affiliation | Centre de Compétence des Maladies Neuromusculaires de Bayonne, France | |
| dc.contributor.affiliation | Centre de Compétence des Maladies Neuromusculaires de Hendaye, France | |
| dc.identifier.doi | 10.1051/medsci/2021190 | |
| dc.identifier.pmid | 34878392 | |