| dc.contributor.author | Aubin, Carl-Eric | - |
| dc.contributor.author | Labelle, Hubert | - |
| dc.contributor.author | Cheriet, Farida | - |
| dc.contributor.author | Villemure, Isabelle | - |
| dc.contributor.author | Mathieu, Pierre A. | - |
| dc.contributor.author | Dansereau, Jean | - |
| dc.date.accessioned | 2014-08-13T07:13:00Z | |
| dc.date.available | 2014-08-13T07:13:00Z | |
| dc.date.issued | 2007 | fr_FR |
| dc.identifier.citation | Aubin, Carl-Eric ; Labelle, Hubert ; Cheriet, Farida ; Villemure, Isabelle ; Mathieu, Pierre A. ; Dansereau, Jean ; Évaluation tridimensionnelle et optimisation du traitement orthopédique de la scoliose idiopathique adolescente, Med Sci (Paris), 2007, Vol. 23, N° 11; p. 904-909 ; DOI : 10.1051/medsci/20072311904 | fr_FR |
| dc.identifier.issn | 1958-5381 | fr_FR |
| dc.identifier.uri | http://hdl.handle.net/10608/6023 | |
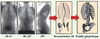
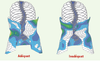
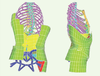
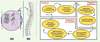
| dc.description.abstract | La scoliose idiopathique adolescente est une maladie complexe du système musculo-squelettique, qui se caractérise par des déformations tridimensionnelles du rachis, de la cage thoracique et du bassin. Les courbures modérées sont généralement traitées à l’aide d’une orthèse thoraco-lombo-sacrée. L’article qui suit présente différents travaux consacrés, au cours des quinze dernières années, à l’évaluation biomécanique et l’optimisation du traitement orthopédique de la scoliose idiopathique adolescente. | fr |
| dc.description.abstract | Adolescent idiopathic scoliosis involves complex tridimensional deformities of the spine, rib cage andpelvis. Moderate curves generally are treated using an orthosis. This paper presents different studies performed over the last fifteen years related to the biomechanical evaluation and optimization of the orthopedic treatment of scoliotic deformities. Patient specific 3D models of the spine, pelvis and rib cage are computed from calibrated radiographs, and are used to calculate 2D and 3D clinical indices. The torso shape is acquired using surface topography. With such internal and external 3D models, the efficacy of the most frequently used orthoses can be analyzed and new treatments can be developed. Pressures generated by a brace on the patient’s trunk were measured using a flexible matrix of pressure sensors and displayed over the patient’s internal geometry in order to analyze the brace efficacy. Patient specific finite element models have been developed, including the osseo-ligamentous structures as well as the muscles, the neuro-control, trunk growth and its adaptation to the stress. These models were used to analyze the effects of the Boston brace. The electro-myographic activity also was measured to analyze the « active » correction mechanisms. Adjustment techniques and software are used to help the orthotists with real time feedback when the brace is being fabricated and adjusted to the patient. Residual growth potential is also being added to the computer model to simulate the long term effect of a brace. The improvement of the orthotic treatments of scoliotic deformities is very encouraging. The exploitation of such tools is expected to allow reaching optimal treatment personalized to each patient. | en |
| dc.language.iso | fr | fr_FR |
| dc.publisher | EDK | fr_FR |
| dc.relation.ispartof | M/S revues | fr_FR |
| dc.rights | Article en libre accès | fr |
| dc.rights | Médecine/Sciences - Inserm - SRMS | fr |
| dc.source | M/S. Médecine sciences [ISSN papier : 0767-0974 ; ISSN numérique : 1958-5381], 2007, Vol. 23, N° 11; p. 904-909 | fr_FR |
| dc.subject.mesh | Adolescent | fr |
| dc.subject.mesh | Orthèses de maintien | fr |
| dc.subject.mesh | Conception d'appareillage | fr |
| dc.subject.mesh | Humains | fr |
| dc.subject.mesh | Orthèses | fr |
| dc.subject.mesh | Scoliose | fr |
| dc.title | Évaluation tridimensionnelle et optimisation du traitement orthopédique de la scoliose idiopathique adolescente | fr |
| dc.title.alternative | Tridimensional evaluation and optimization of the orthotic treatment of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis | en |
| dc.type | Article | fr_FR |
| dc.contributor.affiliation | CHU Sainte-Justine, Montréal (Québec), Canada, Chaire de recherche du Canada « Innovations CAO en génie orthopédique », Chaire de recherche industrielle CRSNG/Medtronic en biomécanique de la colonne vertébrale, École Polytechnique de Montréal, Département de génie mécanique, Case Postale 6079, Succursale Centre-ville, Montréal (Québec), H3C 3A7 Canada | fr_FR |
| dc.contributor.affiliation | CHU Sainte-Justine, Montréal (Québec), Canada, Département de chirurgie, Université de Montréal, Canada | fr_FR |
| dc.contributor.affiliation | CHU Sainte-Justine, Montréal (Québec), Canada, Département de physiologie, Université de Montréal, Canada | fr_FR |
| dc.contributor.affiliation | CHU Sainte-Justine, Montréal (Québec), Canada, Département de génie informatique, École Polytechnique de Montréal, Canada | fr_FR |
| dc.identifier.doi | 10.1051/medsci/20072311904 | fr_FR |
| dc.identifier.pmid | 18021698 | fr_FR |