| dc.contributor.author | Buyse, Marion | - |
| dc.contributor.author | Aparicio, Thomas | - |
| dc.contributor.author | Guilmeau, Sandra | - |
| dc.contributor.author | Goïot, Hélène | - |
| dc.contributor.author | Sobhani, Iradj | - |
| dc.contributor.author | Badot, André | - |
| dc.date.accessioned | 2014-03-04T10:36:55Z | |
| dc.date.available | 2014-03-04T10:36:55Z | |
| dc.date.issued | 2004 | fr_FR |
| dc.identifier.citation | Buyse, Marion ; Aparicio, Thomas ; Guilmeau, Sandra ; Goïot, Hélène ; Sobhani, Iradj ; Badot, André ; Effets paracrines de la leptine produite par l’estomac, Med Sci (Paris), 2004, Vol. 20, N° 2; p. 183-188 ; DOI : 10.1051/medsci/2004202183 | fr_FR |
| dc.identifier.issn | 1958-5381 | fr_FR |
| dc.identifier.uri | http://hdl.handle.net/10608/5161 | |
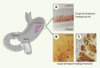
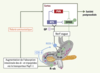
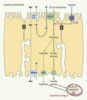
| dc.description.abstract | La leptine, produit du gène ob, est une protéine de 16 kDa qui agit par des mécanismes centraux pour contrôler l’équilibre énergétique. Outre le tissu adipeux, d’autres organes dont l’estomac produisent également la leptine. Les récepteurs de la leptine ont été identifiés dans le tractus digestif, notamment dans l’estomac, l’intestin, le foie, le pancréas. Les études récentes suggèrent que la leptine gastrique puisse agir localement sur de nouvelles cibles pour contrôler les fonctions intestinales d’absorption, de sécrétion et de développement. De plus, elle pourrait jouer un rôle dans la physiopathologie intestinale. Cet article résume les données expérimentales suggérant que la leptine soit une nouvelle hormone du tractus gastro-intestinal. | fr |
| dc.description.abstract | Leptin, a 16 kilodalton protein-encoded by the ob gene, is involved in the regulation of food intake, body composition, and energy expenditure through a central feedback mechanism. Initially thought to be adipocyte-specific, the ob gene, as well as the leptin receptor, has been found in a variety of other tissues. Relevant to this review, the leptin gene and its receptor have been identified in the stomach, intestine, liver, and pancreas. Recent data also suggest that gut leptin may act locally within the gastrointestinal tract to influence intestinal functions such as nutrient absorption and may have a physiopathological implication. This review emphasises the concept that leptin may be a new gastrointestinal hormone. | en |
| dc.language.iso | fr | fr_FR |
| dc.publisher | EDK | fr_FR |
| dc.relation.ispartof | M/S revues | fr_FR |
| dc.rights | Article en libre accès | fr |
| dc.rights | Médecine/Sciences - Inserm - SRMS | fr |
| dc.source | M/S. Médecine sciences [ISSN papier : 0767-0974 ; ISSN numérique : 1958-5381], 2004, Vol. 20, N° 2; p. 183-188 | fr_FR |
| dc.subject.mesh | Animaux | fr |
| dc.subject.mesh | Colite | fr |
| dc.subject.mesh | Humains | fr |
| dc.subject.mesh | Absorption intestinale | fr |
| dc.subject.mesh | Leptine | fr |
| dc.subject.mesh | Estomac | fr |
| dc.title | Effets paracrines de la leptine produite par l’estomac | fr |
| dc.type | Article | fr_FR |
| dc.contributor.affiliation | Inserm U.410, IFR02 Claude Bernard, UFR Xavier Bichat, 16, rue Henri Huchard, BP 416, 75870 Paris Cedex 18, France | fr_FR |
| dc.identifier.doi | 10.1051/medsci/2004202183 | fr_FR |
| dc.identifier.pmid | 14997438 | fr_FR |