| dc.contributor.author | Coux, O | fr_FR |
| dc.contributor.author | Piechaczyk, M | fr_FR |
| dc.date.accessioned | 2012-08-30T12:32:52Z | |
| dc.date.available | 2012-08-30T12:32:52Z | |
| dc.date.issued | 2000 | fr_FR |
| dc.identifier.citation | Coux, O ; Piechaczyk, M, Le système ubiquitine/protéasome : un ensemble (de) complexe(s) pour dégrader les protéines., Med Sci (Paris), 2000, Vol. 16, N° 5; p.623-9 | fr_FR |
| dc.identifier.issn | 1958-5381 | fr_FR |
| dc.identifier.uri | http://hdl.handle.net/10608/1705 | |
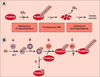
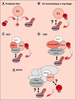
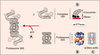
| dc.description.abstract | Le système
ubiquitine/protéasome joue un
rôle majeur dans la protéolyse
intracellulaire. De nombreux
composants de ce système sont
des complexes protéiques dont
l’architecture multimérique et
modulaire permet l’intégration
fonctionnelle de plusieurs
activités enzymatiques dans une
même structure (protéasome) ou
le partage d’un même module
fonctionnel par plusieurs
protéines (enzymes
d’ubiquitinylation). Ces propriétés
concourent à l’étonnante
efficacité et à l’extraordinaire
spécificité de cette voie
protéolytique. | fr |
| dc.description.abstract | Intracellular proteolysis is an essential cell function. In addition to the elimination of abnormal or excess proteins, it is involved in the control of major cell processes such as division, differentiation, apoptosis, the response to numerous external stimuli and the production of antigenic peptides. In eucaryotes, the ubiquitin/proteasome pathway plays a major part in the destruction of intracellular proteins and functions in two steps. First, substrates are marked by covalent attachment of chains of a small protein, ubiquitin, owing to a complex cascade of enzymes. Some of these enzymes are hetero-multimeric complexes sharing common functional modules. In a second step, ubiquitinated proteins are recognized and degraded by the 26S proteasome which constitute the proteolytic machinery of the system. This review describes the components of this pathway as well as the mechanisms underlying its extraordinary efficiency and selectivity in the light of the most recent discoveries. | en |
| dc.language.iso | fr | fr_FR |
| dc.publisher | Masson, Paris | fr_FR |
| dc.rights | Article en libre accès | fr |
| dc.rights | Médecine/Sciences - Inserm - SRMS | fr |
| dc.source | M/S. Médecine sciences [revue papier, ISSN : 0767-0974], 2000, Vol. 16, N° 5; p.623-9 | fr_FR |
| dc.title | Le système ubiquitine/protéasome : un ensemble (de) complexe(s) pour dégrader les protéines. | fr |
| dc.title.alternative | The ubiquitin/proteasome pathway. | fr_FR |
| dc.type | Article | fr_FR |
| dc.contributor.affiliation | Centre de recherche en biochimie macromoleculaire, Cnrs, 1919, route de Mende, 34293 Montpellier, France; Institut de genetique moleculaire, IFR24, Cnrs, 1919, route de Mende, 34293 Montpellier, France | - |
| dc.identifier.doi | 10.4267/10608/1705 | |